Credential Intelligence - Defense in Depth Dashboard
The Credential Intelligence - Defense in Depth dashboard overviews the number of compromised credentials on your applications. Compromised credentials represent your users’ authentication information, such as a username and password, that are likely known by bad actors. Credential Intelligence monitors your applications’ authentication endpoints for suspicious behavior, then flags any at-risk credentials for your review. By utilizing the Credential Intelligence dashboard, you can quickly recognize and mitigate compromised credentials before users’ accounts are affected.
You can access the dashboard from Credential Intelligence > Explore > Dashboard.
The Credential Intelligence dashboard retains data for up to 14 months. HUMAN hashes, salts, and stores compromised credentials in our database. These credentials do not expire and are not exposed in the HUMAN console. You can request that HUMAN deletes these logs within 60 days.
You can learn more about the data presented in the dashboard with this article.
Filters
You can apply filters to the Credential Intelligence dashboard to customize the data that appears. Filters apply to the entire dashboard.
![]()
There are a variety of filters available:
- Traffic Type: Filter by where the traffic came from, such as from web or native mobile applications.
- Applications: Filter by the applications you’ve created in HUMAN.
- Use case: Filter by the type of authentication request.
- Time Range: Filter by a specified time period.
Metrics
There are four major metrics at the top of the dashboard that summarize login attempts and compromised credentials on your applications.
- Login & Authentication Requests: The total number of login and authentication requests on your applications.
- Malicious Requests: The number of authentication requests that Credential Intelligence detected were made by bots using compromised credentials.
- Credentials at Risk: The number of credentials Credential Intelligence has flagged as at risk, but not necessarily compromised.
- Compromised Accounts: The number of accounts that passed authentication requests using compromised credentials.
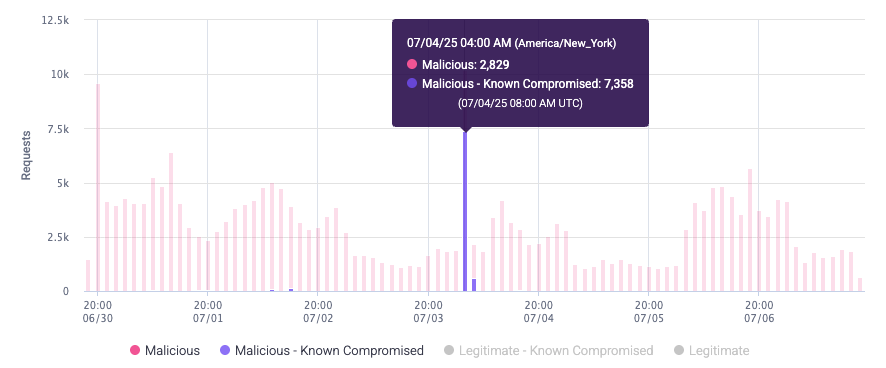
Requests Analysis
The Requests Analysis section shows all authentication requests over time on your applications. Credential Intelligence separates requests by malicious, known compromised, and legitimate requests. This is useful for quickly seeing unusual malicious authentication activity such as a sudden spike in malicious requests.
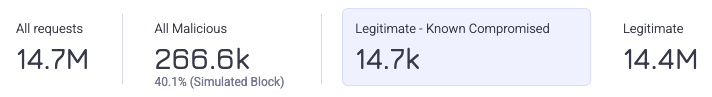
Statistics
Quick statistics are shown at the top of Requests Analysis. These summarize the types of requests Credential Intelligence detected on your application.
We recommend minimizing the number of Legitimate - known compromised accounts by asking these users to reset their password. These represent your attack surface area, which are accounts that are currently safe, but vulnerable. We recommend taking mitigating actions to secure these accounts where possible.
- All requests: The total number of login and authentication requests over the time period.
- All malicious: The number of authentication requests that Credential Intelligence detected were made by bots using compromised credentials.
- Legitimate - known compromised: The number of legitimate authentication requests that were made using compromised credentials.
- Legitimate: The number of legitimate authentication requests.
Graph
The Requests Analysis graph shows each type of authentication request over time. You can click each type at the bottom of the graph to add or remove it from view. Credential Intelligence groups requests that occurred at approximately the same time so you can more easily see the distribution of the types of requests over time.
You can also hover over activity to see a detailed summary of requests made at that time. Malicious - Known Compromised accounts represent the combined value of Bot Mitigation and Credential Intelligence capabilities.
Credentials Analysis
The Credentials Analysis section shows the number of compromised credentials over time. Credential Intelligence separates credentials by malicious and legitimate compromised credentials. This is useful for tracking the number of compromised credentials over time and helps you take action if there’s unusual malicious activity.
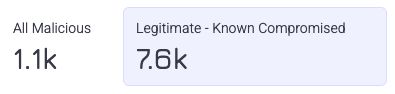
Statistics
Quick statistics are shown at the top of Credentials Analysis. These summarize the number of compromised credentials by type on your application.
- All Malicious: The total number of malicious compromised credentials Credential Intelligence has detected over the time period. Credential Intelligence considers compromised credentials as malicious if it detects that a bad actor attempted to use them. Malicious credentials are further separated into two types:
- Malicious - Newly Observed: Credentials that were not previously in Credential Intelligence’s database, but newly detected as being used by malicious attackers, and are then added to the compromised credentials database.
- Malicious - Known Compromised: Credentials that Credential Intelligence already has previously identified as compromised by bad actors.
- Legitimate - Known Compromised: The total number of credentials that Credential Intelligence detects as compromised, but have only been used in legitimate requests so far.
Graph
The Credentials Analysis graph shows each type of compromised credentials over time. You can click each type at the bottom of the graph to add or remove it from view. Credential Intelligence groups credentials it detects at approximately the same time so you can more easily observe the distribution of the types of credentials over time. You can hover over a compromised credentials type to see a detailed summary of credentials at that time.

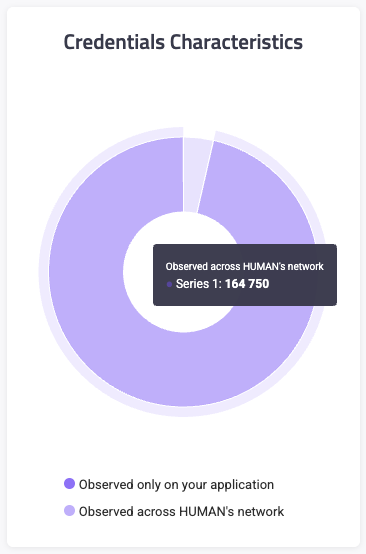
Credentials Characteristics
The Credentials Characteristics chart shows the distribution of compromised credentials Credential Intelligence detected directly on your applications as compared to the compromised credentials detected across HUMAN’s customer network. HUMAN observes credential stuffing attacks on our customers across the web, and we flag any compromised credentials that are used in these attacks. Note that HUMAN hashes, salts, and stores compromised credentials in our database. These credentials do not expire and are not exposed in the HUMAN console. You can request that HUMAN deletes these logs within 60 days
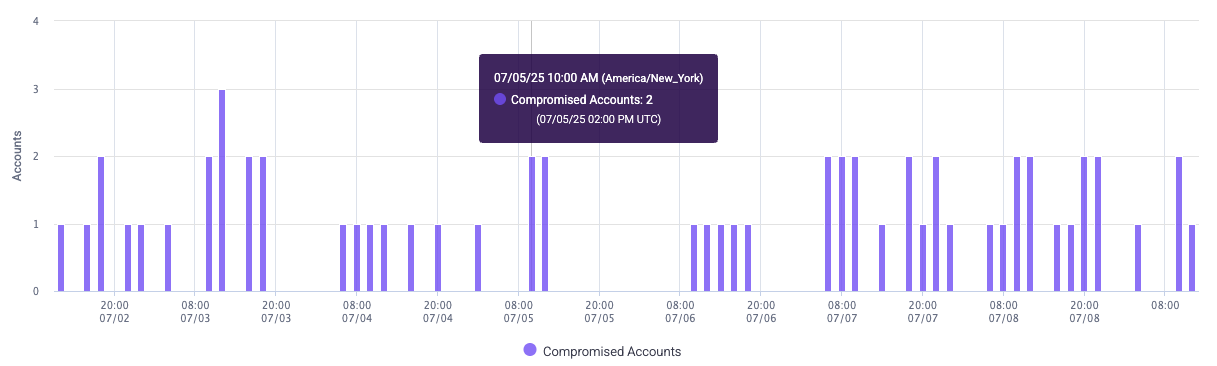
Accounts Analysis
The Accounts Analysis section shows the number of compromised accounts over time. Credential Intelligence considers an account as compromised if it detects a bad actor using compromised credentials to access an account. This is useful for tracking the number of affected accounts on your applications at a time so you can take appropriate mitigating actions for your users.
If you do not see data in this section, be sure to complete our integration guide so you send the appropriate parameters to HUMAN’s Sensor and Enforcer. Compromised accounts only appear here based on information sent on additional_s2s activity, which is configured in the Enforcer.
Statistics
Accounts Analysis features the Compromised Accounts statistic, which is the number of accounts that were accessed by bad actors using compromised accounts.
Graph
The Accounts Analysis graph shows compromised accounts over time. Credential Intelligence groups the accounts it detects at approximately the same time so you can more easily observe the distribution over time. Hover over a bar in the graph to see a detailed summary of compromised accounts at that time.