Configuration
Overview
All HUMAN Enforcer configurations can be set using the properties specified in the JS-ConfigureAndInitialize.xml policy inside the preflow-enforce shared flow.
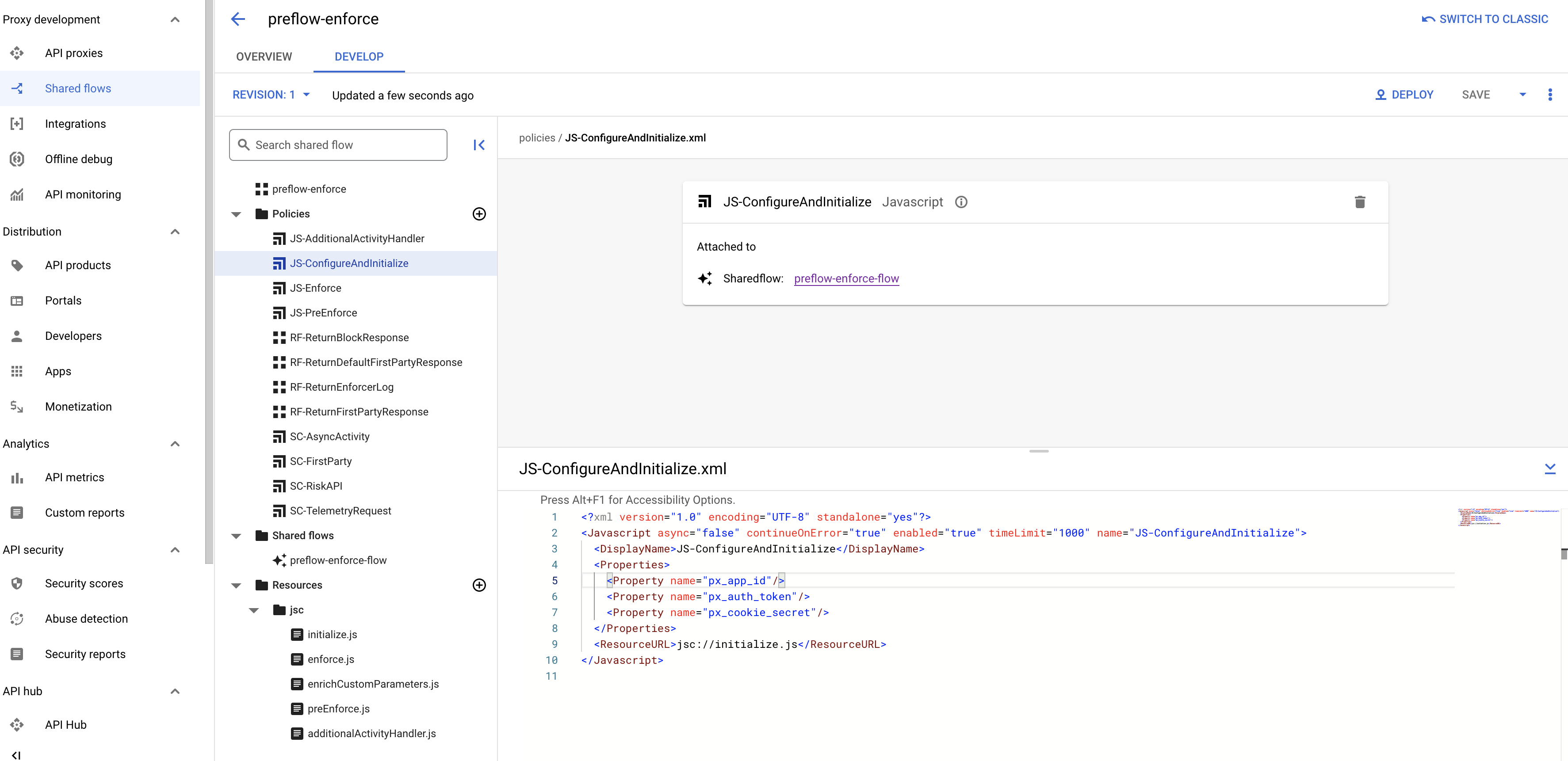
Configuration
An object of configuration values that dictate the behavior of the Apigee Edge Enforcer flow. The following properties should be configured according to your Apigee Edge setup.
Required values:
- px_app_id
- px_auth_token
- px_cookie_secret
px_app_id (Required Property)
The application ID. Required Property.
px_auth_token (Required Property)
The token used for authorization with the HUMAN backend. Required to create a new instance of the HumanSecurity class.
px_cookie_secret (Required Property)
The secret used to encrypt and decrypt the risk cookie.
px_module_enabled
This boolean serves as an on/off switch for the entire module, providing a way to enable and disable all enforcer capabilities quickly and easily.
Default: true
px_module_mode
This feature controls the behavior of the enforcer by changing how it executes certain parts of the workflow. Most notably, different modes allow for analysis and fine-tuning of the enforcer behavior without serving block pages that affect end users.
Possible values:
"monitor"- the enforcer will perform all functions without returning block responses"active_blocking"- the enforcer will return block responses when needed
Default: "monitor"
px_logger_severity
The verbosity of the logs generated by the enforcer.
Possible values:
"none"- No logs will be generated"error"- Sparse logs will be generated only when errors occur"debug"- Detailed logs will always be generated (not advisable for production environments)
Default: "error"
px_ip_headers
By default, the IP is taken from the proxy.client.ip variable. However, if this header is inaccurate, the enforcer can extract the IP from the headers configured here. The headers are traversed in the order they are listed. The first header value that exists will be used as the client IP. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_advanced_blocking_response_enabled
In specific cases (e.g., XHR post requests), a full CAPTCHA page render might not be an option. In such cases the advanced blocking response returns a JSON object containing all the information needed to render a customized captcha challenge implementation - be it a popup modal, a section on the page, etc. This allows for flexibility and customizability in terms
of how the captcha pages are displayed.
Default: true
px_first_party_enabled
To prevent suspicious or unwanted behavior on the client side, some browsers or extensions (e.g., adblockers) may deny the frontend JavaScript code from making requests to other domains. This prevents the HUMAN sensor from making requests to the HUMAN backends, which greatly limits HUMAN’s detection capabilities. To avoid this problem, first party enables the enforcer to be used as a proxy for HUMAN servers, and to serve content to the browser from a first party endpoint (i.e., an endpoint on the customer’s domain).
Default: true
px_custom_first_party_prefix
By default, first party endpoints always begin with the application ID without the initial “PX”. For example, if the application ID is PX12345678, then all first party routes will take the form /12345678/*. This configuration sets a custom prefix for first party routes to use in addition to the default prefix. When configured, the enforcer will respond to first party requests with endpoints matching the patterns /<px_custom_first_party_prefix>/init.js, /<px_custom_first_party_prefix>/xhr/*, and /<px_custom_first_party_prefix>/captcha/*.
Default: "" (when empty, will use the default as described above)
px_custom_first_party_sensor_endpoint
For an application with ID PX12345678, the first party sensor endpoint is /12345678/init.js by default. This configuration customizes the entire first party sensor script endpoint. Note that in addition to responding to requests that match this configured route, the enforcer will also proxy first party requests that match the default pattern (/12345678/init.js) and patterns according to the custom prefix (/<px_custom_first_party_prefix>/init.js) if one is configured.
Default: ""
px_custom_first_party_xhr_endpoint
For an application with ID PX12345678, the first party XHR endpoint is /12345678/xhr by default. This configuration customizes the first party XHR endpoint. Note that in addition to responding to requests that match this configured route, the enforcer will also proxy first party requests that match the default pattern (/12345678/xhr/*) and patterns according to the custom prefix (/<px_custom_first_party_prefix>/xhr/*) if one is configured.
Default: ""
px_custom_first_party_captcha_endpoint
For an application with ID PX12345678, the first party captcha endpoint is /12345678/captcha by default. This configuration customizes the first party captcha endpoint. Note that in addition to responding to requests that match this configured route, the enforcer will also proxy first party requests that match the default pattern (/12345678/captcha/*) and patterns according to the custom prefix (/<px_custom_first_party_prefix>/captcha/*) if one is configured.
Default: ""
px_bypass_monitor_header
When enabling the Enforcer for the first time, it is recommended to do so in monitor mode to collect data before actually starting to block user requests. Prior to switching the module mode to active_blocking entirely, it’s also crucial to verify that the full blocking flow works as expected. This feature activates the full blocking flow even while in monitor mode if a particular header is present on the request.
Default: ""
px_enforced_routes
Customers may want certain, but not all, endpoints to be enforced by HUMAN, even when the Enforcer is in the Monitor mode. These routes will go through the full enforcer workflow, including blocking requests when necessary. That is, even when the enforcer is in monitor mode, these defined routes will behave as if in active blocking mode. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_monitored_routes
Enables certain endpoints to be monitored rather than enforced by HUMAN, even when the Enforcer is in the Active Blocking mode. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_sensitive_headers
The HUMAN Detector requires information about the HTTP request as part of its bot detections. Certain headers may contain information that should not be forwarded to other servers, including the HUMAN backend. Configuring these header names as sensitive headers will remove these headers from requests sent to other backends by HUMAN. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: "cookie,cookies"
px_sensitive_routes
Certain endpoints may require more stringent protection from bot attacks (e.g., endpoints that execute payments or handle personal information). In these cases, routes can be configured as sensitive routes, meaning risk API calls will be made even if the request contains a valid, unexpired cookie. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_filter_by_extension
HUMAN does not enforce static assets such as images and documents. To prevent unnecessary API calls to HUMAN servers and needless computation, the enforcer filters all requests with a valid static file extension. Filtering by extension only applies to HTTP requests with methods GET and HEAD. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ".css,.bmp,.tif,.ttf,.docx,.woff2,.js,.pict,.tiff,.eot,.xlsx,.jpg,.csv,.eps,.woff,.xls,.jpeg,.doc,.ejs,.otf,.pptx,.gif,.pdf,.swf,.svg,.ps,.ico,.pls,.midi,.svgz,.class,.png,.ppt,.mid,.webp,.jar,.json,.xml"
px_filter_by_http_method
Filters out requests according to their HTTP method, avoiding unnecessary traffic in the enforcer verification flow and reducing operating costs. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_filter_by_ip
Filters out requests according to their IP address, avoiding unnecessary traffic in the enforcer verification flow and reducing operation costs. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_filter_by_route
Route prefixes (endpoints) specified here will not be blocked, regardless of the score they receive. A request to a filtered route will not generate any risk or async activities. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_filter_by_user_agent
Filters out requests according to their user agent value, avoiding unnecessary traffic in the enforcer verification flow and reducing operation costs. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_css_ref
Provides a way to include an additional custom .css file to add to the block page.
Default: ""
px_js_ref
Provides a way to include a custom JS script to add to the block page. This script will run after the default JS scripts.
Default: ""
px_custom_logo
Adds a custom logo to the block page that will be shown to users. This aligns the block page with the customer’s brand.
Default: ""
px_custom_cookie_header
The Enforcer attempts to extract the HUMAN cookies from the ‘Cookie’ header. If the HUMAN cookies are transferred on a header other than ‘Cookies’, the header name should be configured here.
Default: "x-px-cookies"
px_user_agent_max_length
The maximum length of the User-Agent header. If the user agent header value exceeds this length, it will be truncated to this length prior to processing.
Default: 8528
This value should not be changed without consulting with the HUMAN Customer Success team.
px_cors_support_enabled
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a mechanism that enables the server to indicate when a request contains cross-origin resources. It does so by adding special HTTP headers to the request, which permits the browser to load these resources. Without these headers, the browser may block requests to these resources for security reasons.
In most cases, CORS employs a two-stage procedure with a preliminary “preflight” request followed by the actual request. The preflight request checks if the actual request will be responded to. To learn more about different request types, see these examples.
In the Enforcer, CORS behavior must be configured to address both simple requests (without preflight) and more complex ones (with preflight). Enabling CORS support via this configuration will have the following effects:
- It will automatically add the following default CORS response headers to block responses resulting from CORS requests.
- It will activate the
px_cors_preflight_request_filter_enabledconfiguration, which allows for filtering preflight requests.
Default: false
Custom CORS Block Headers
If the default CORS response headers are not sufficient, it is possible to customize the headers that should be added to all block responses resulting from CORS requests. This can be set in the Assign Message policy named AM-CustomCorsBlockResponseHeaders in the Preflow-Enforce shared flow. See here for more information about the Assign Message policy.
px_cors_preflight_request_filter_enabled
This configuration disables enforcement for CORS preflight requests. When this configuration is set to true, CORS preflight requests will be filtered from the enforcer flow. That is, they will pass through the enforcer flow without triggering detection or block responses.
Default: false
px_additional_activity_handler
The additional activity handler is a custom function passed to the enforcer. The enforcer runs this callback after sending page_requested or block activity to the collector, and before forwarding the request to the next step in the pipeline. A common use case of the additional activity handler is to set the score as a variable or header. Then the application can read the score and do what is defined within the application’s logic.
This custom function can be configured in the additionalActivityHandler.js resource file in the Preflow-Enforce shared flow. Note that only the contents of the px_additional_activity_handler function should be modified.
Default: null
px_enrich_custom_parameters
This custom function enriches activities sent from the enforcer to HUMAN with additional custom data. This data can include user information, session IDs, or other data that HUMAN should have access to. These custom parameters are defined by a configurable function that must return an object that contains these custom parameters. There is a limit of 10 custom parameters.
This custom function can be configured in the enrichCustomParameters.js resource file in the Preflow-Enforce shared flow. Note that only the contents of the px_enrich_custom_parameters function should be modified.
Default: null
Account Defender Configurations
px_jwt_cookie_name
The name of the cookie that contains the JWT token from which user identifiers should be extracted.
Default: ""
px_jwt_cookie_user_id_field_name
The field name in the JWT object, extracted from the JWT cookie, that contains the user ID to be extracted and reported.
Default: ""
px_jwt_cookie_additional_field_names
The field names in the JWT object, extracted from the JWT cookie, that should be extracted and reported in addition to the user ID. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
px_jwt_header_name
The name of the header that contains the JWT token from which user identifiers should be extracted.
Default: ""
px_jwt_header_user_id_field_name
The field name in the JWT object, extracted from the JWT header, that contains the user ID to be extracted and reported.
Default: ""
px_jwt_header_additional_field_names
The field names in the JWT object, extracted from the JWT header, that should be extracted and reported in addition to the user ID. This should be configured as a comma-separated list.
Default: ""
Credential Intelligence Configurations
px_login_credentials_extraction_enabled
This enables the extraction and reporting of credentials from the Enforcer. This must be set to true to enable the Credential Intelligence product.
Default: false
px_login_credentials_extraction
An array of configurations for each credential endpoint. Each element in the array is a JSON object representing a distinct endpoint to which credentials are sent, and includes information about how to identify these credential-bearing requests, how to extract the credentials from the request, and how to determine if the request operation (login, signup, etc.) was successful based on the returned HTTP response.
Default: []
Each credential endpoint configuration object contains the following fields:
path
Required. The path of the request that contains the credentials. It can be either an exact path or a string in the form of a regular expression.
path_type
Optional. Whether the incoming request path should be evaluated against the configured path as a regular expression or as an exact match.
Possible values:
"exact"- The value set inpathmust match the request path exactly as is."regex"- The value set inpathrepresents a regular expression to be matched against the request path.
Default: "exact"
method
Required. The HTTP method of the request that contains the credentials. This can be set to any string representing an HTTP method (e.g., "GET", "POST", "PUT").
sent_through
Required. Whether the credentials should be extracted from the request headers, query parameters, body, or via a defined custom callback.
Possible values:
"body"- The credentials will be extracted according to the configureduser_fieldandpass_fieldvalues from the request body."header"- The credentials will be extracted from the request headers according to the configureduser_fieldandpass_field."query-param"- The credentials will be extracted from the query parameters according to the configureduser_fieldandpass_field.
Sent Through Body: Content Types
If "body" is configured as the sent_through value, the Enforcer must read and parse the incoming request body. The Enforcer parses the request body based on the Content-Type request header.
Supported content types are listed below.
application/jsonapplication/x-www-form-urlencodedmultipart/form-data
user_field
Required. The name of the field, header name, or query parameter where the username can be found.
pass_field
Required. The name of the field, header name, or query parameter where the password can be found.
Nested Objects in a JSON Body
The user_field and pass_field configurations support subfields in cases of Content-Type: application/json bodies with nested objects. The subfields can be separated with periods.
For example, the credential endpoint configuration object can include a user_field with the value "user_info.username" and a pass_field with the value "authentication.password" to support extracting the credentials from the following JSON body:
protocol
Optional. Whether to process credentials as part of single or multiple HTTP requests. By default, the module tries to process requests depending on which credential fields were extracted.
Possible values:
"v2"- Both username and password are present on the same HTTP request and must be extracted successfully to trigger Credential Intelligence."multistep_sso"- The username and password are delivered on different HTTP requests. Either the username or password, but not both, must be extracted successfully to trigger Credential Intelligence."both"- The username and password may be present on the same HTTP request or on different HTTP requests. If either username or password is successfully extracted, the Enforcer will send the credentials according to themultistep_ssoprotocol. If both username and password are successfully extracted, the Enforcer will send the credentials according to thev2protocol.
Default: "both"
login_successful_reporting_method
Required. The method by which the Enforcer will determine whether the login request was successful.
Possible values:
"status"- The Enforcer will determine if the login request was successful by evaluating the response status code against thelogin_successful_statusesconfiguration."body"- The Enforcer will determine if the login request was successful by evaluating the response body content against thelogin_successful_body_regexconfiguration."header"- The Enforcer will determine if the login request was successful by evaluating the response headers against thelogin_successful_header_nameandlogin_successful_header_valueconfigurations.
Default: "status"
login_successful_statuses
Optional. An array of HTTP statuses signifying a successful login. All other status codes will be treated as unsuccessful login attempts. Takes effect only when the login_successful_reporting_method is set to "status".
Default: [200]
login_successful_body_regex
Required only if login_successful_reporting_method is set to "body". A regular expression (or string representing a regular expression) to against which the response body will be evaluated. A match indicates a successful login.
Default: ""
login_successful_header_name
Required only if login_successful_reporting_method is set to "header". A response header name signifying a successful login response. If the login_successful_header_value field is empty or not configured, any response containing this header name will be considered a successful login. If the login_successful_header_value is configured, the response header value must be an exact match.
Default: ""
login_successful_header_value
Optional. If this value is configured, a login attempt will be considered successful only if the response contains a header name matching the login_successful_header_name, and whose value is exactly equal to this configuration value. Takes effect only when the login_successful_reporting_method is set to "header".
Default: ""
px_compromised_credentials_header
The header name to be set on the incoming request if the credentials are compromised. If this header is added, its value will always be 1. If credentials have not been identified as compromised, the header will not be added to the request.
Default: "px-compromised-credentials"
px_send_raw_username_on_additional_s2s_activity
Whether to report the raw username on the additional_s2s activity. When set to false, the raw username will never be reported. When set to true, the raw username will only be reported if (1) the credentials are compromised, and (2) the login request was successful.
Default: false
px_automatic_additional_s2s_activity_enabled
Whether to send the additional_s2s activity, which reports on whether the login was successful, automatically in the postEnforce function. This should only be set to false if it is not possible to determine whether the login was successful based on the HTTP response. This means the additional_s2s activity must be sent in some other way.
Default: true
px_additional_s2s_activity_header_enabled
Whether to attach the additional_s2s payload and URL as headers to the original request. This is done so that the additional_s2s activity can be enriched with the proper login_successful value and sent to the provided URL at a later stage. This should only be enabled if the px_automatic_additional_s2s_activity_enabled is set to false.
When set to true, the following headers are added to the origin request:
px-additional-activity- A JSON object containing the payload of theadditional_s2sactivity. Thelogin_successfulandhttp_status_codefields should be set prior to sending the activity.px-additional-activity-url- The URL to which theadditional_s2spayload should be sent as an HTTP POST request.
Default: false
Below is an example of JavaScript code at the origin server to handle parsing, enrichment, and sending of the additional_s2s activities that arrive on request headers.