Human Challenge Customizations and Configurations
Challenge Configuration
To view and modify the challenge settings in the portal, go to the “Challenge Settings” under the Bot Defender “Product Setting” section.

Enabling Auto ABR (Advanced Blocking Response)
To enable the Advanced Blocking Response, turn on the ABR toggle, and click “Save Changes”. When “Auto-ABR” is on, the HUMAN Web Sensor will automatically display the challenge overlay for any API requests sent by the web browser outside of the page request and rendering process. See our documentation for further details.
Enabling Enhanced Accessibility Mode
To enable the Enhanced Accessibility Mode, turn on the toggle, and click “Save Changes”. When “Enhanced Accessibility Mode” is on, the HUMAN Web Sensor will automatically display the accessible version of the HUMAN challenge. See our documentation for further details. Please allow up to 10 minutes for this change to take effect.
Enabling the “Enhanced Accessibility Mode” in production
Before enabling Enhanced Accessibility Mode, we recommend testing this version with existing customizations on a staging environment before using it in production. Please note that any customizations you make may cause issues with accessibility guidelines.
Challenge Look & Feel
- Human Challenge provides customization options for the user interface.
- The interface allows the customer:
- Changing the color and style of the Challenge button and its surroundings.
- Adding Text translations and localization.
- The challenge can be customized by setting the customization object on the window object in the CAPTCHA page.
- The customization code itself is injected as a remote script in the block page HTML.
- The script path can be set via the px_js_ref configuration property on the Enforcer side, please make sure it is an absolute path.
For more information on the Look & Feel customization, please see our Human Challenge Console Customization Tool
Customizing ABR
Customizing ABR (Advanced Blocking Response)
When attempting to Customize ABR, make sure the object is set on the window within the website pages for which you will present a challenge.
Here is an example of a snippet to set the customization object on the window (Detailed options will follow below):
Human Challenge Language
Forcing a specific locale translation

To force a specific locale translation regardless of browser’s identified locale, set the following field on the window.
This will translate all texts to the specified language, otherwise texts will be translated according to the browser’s identified locale.
A list of supported language codes can be found below.
For Old block pages - this will only translate the challenge button itself, read further for instructions on translating the rest of the page.
Custom translation
To define your own custom translations for languages, you will need to add to the configuration object, set on the window.
A few options here:
- You can define the default object - forcing the translation you define here to appear regardless of the browser’s identified locale.
- Redefine some or all of the locale translations (see list of supported locales below).
When configuring custom translations, we recommend using ctx_hdr instead of headerText. headerText will override other translations and should only be used when other translations are not applied.
Setting default translation example (change texts as you wish):
Setting custom language translations example:
Translating old challenge Pages

To force a specific locale translation regardless of browser's identified locale, set the following field: window._pxSelectedLocale =<languageCode>;
For Old block pages this will only automatically translate the challenge itself, you will need to provide the rest of the translations text as detailed below
Old challenge page translations are achieved by:
- Defining translations for the challenge button ( challenge -> translation, on configuration object)
- Defining translations for the rest of the page (translation, on the configuration object).
To define translations for texts for the rest of the page - define the css selector for the element, as well as the translated text (see examples)
Setting default translation example (Old block pages):
Setting custom language translations example (Old Block pages):
Supported languages:
Human Challenge default language is English (en).
We support the following languages out-of-the-box:
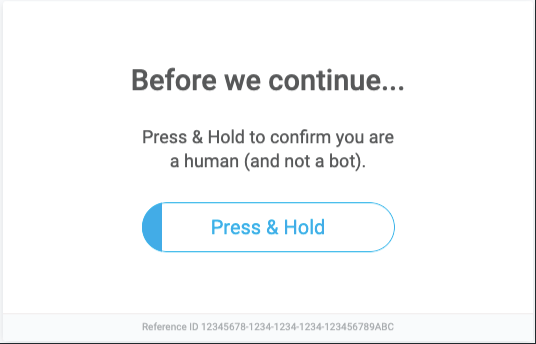
Customizing Human Challenge Look and Feel
Here is an example of the default Challenge page:
Default Context Configuration
The context object defines the look and feel for the button surroundings.
This example demonstrates the default options for the context properties which can be modified.
Challenge Button Customization
The view object defines the look and feel for the challenge button
Height, width and sizes are in pixels.
Here is an example showing the default settings for the view object:
Older block pages have the following default configuration for the view object:
Customers who already provide a challenge customization object should note that upgrading to the new Enforcer version which supports the updated challenge page may result in different outputs.
More button customization options
In the following example we detail all possible customization properties for the button:
Complete examples
Here is a Full configuration example:
And here is a custom configuration example (See the result below):
Which results with:

Behavior Configuration
Callback Function
Add the _pxOnCaptchaSuccess callback function to the window object (mostly used for [Advanced Blocking Response (ABR)](Advanced Blocking Response (ABR) implementation). The function is called when the Challenge is solved, and returns a single parameter indicating if it was solved successfully or not:
If you wish to add the callback to a mobile app challenge (for example, React Native webview), use the _pxOnMobileCaptchaSuccess callback instead of _pxOnCaptchaSuccess. The callback signature and usage are identical.
Post solve behavior
After a valid Captcha solve, if the callback function is defined, we will simply call it. In case the callback function is not defined, the Captcha will execute its default behavior, which usually means a simple page reload. The only exception is when a “url” query-param is included in the page URL, in which case the page will change its URL instead (relative URL is supported). Note that the value of the “url” param is expected to be in base64 (e.g. “https://www.example.com?url=YWJj” will redirect to “https://www.example.com/abc”).
Enforcers
The updated challenge page is supported on all HUMAN Enforcers.